Introduction
The pursuit of renewable energy sources has gained immense momentum in recent years, and one of the most popular and accessible options is solar power. Karnataka, a state in southern India, has been at the forefront of the solar energy revolution. Home to numerous solar power projects, Karnataka has witnessed a surge in residential and commercial installations of solar panels. In this blog, we will explore the financial aspects of installing solar panels in Karnataka. We will answer the pressing question: How much can you save by harnessing the power of the sun in this vibrant state?
Understanding Solar Panels and Savings
Before we delve into the specifics of solar savings in Karnataka, it’s important to understand how solar panels work and how they translate into financial savings.
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic panels, are designed to convert sunlight into electricity. They consist of solar cells that generate direct current (DC) electricity when exposed to sunlight. This electricity is then converted into alternating current (AC) for use in homes and businesses.
The key factors that influence savings from solar panels are as follows:
1. Energy Production: The amount of electricity your solar panel system generates is a critical factor in determining savings. This depends on the size and efficiency of the system.
2. Energy Usage: The electricity generated by the solar panels can be used to offset your energy consumption. The more energy you use, the more you can potentially save.
3. Electricity Rates: The cost of electricity from your utility company plays a significant role. Higher electricity rates can lead to greater savings.
4. Monthly Electric Bill: Your monthly electric bill is a direct representation of your energy usage and costs.
5. Upfront Costs: The initial investment in purchasing and installing solar panels affects your payback period and long-term savings.
6. Tax Credits and Incentives: Government incentives, tax credits, and rebates can significantly reduce the upfront costs of solar installation.
7. Net Metering: Net metering allows you to feed excess electricity back into the grid and receive credits on your utility bill.
Savings Potential in Karnataka
Karnataka boasts abundant sunlight, making it an ideal location for solar installations. The state has implemented policies and incentives to promote the adoption of solar power. Here’s a closer look at the key factors that determine the savings potential for solar in Karnataka:
1. Sunlight Availability: Karnataka receives ample sunlight throughout the year, ensuring high energy production from solar panels.
2. Electricity Rates: The state’s electricity rates are relatively high, making the savings from solar more attractive.
3. Renewable Energy Policies: Karnataka has introduced policies and regulations to encourage the use of solar power, including net metering.
4. Tax Credits and Incentives: The state and central governments offer various incentives, such as capital subsidies, accelerated depreciation, and tax benefits, to reduce the upfront costs of solar installations.
5. Net Metering: Karnataka has a net metering policy that allows solar system owners to feed excess electricity back into the grid and earn credits on their utility bills.
Calculating Solar Savings
To estimate your potential savings from installing solar panels in Karnataka, follow these steps:
1. Determine Your Energy Usage: Review your monthly electric bills to understand your energy consumption.
2. Assess Solar Potential: Evaluate your location’s solar potential, considering factors like sunlight hours and shading.
3. Select Solar Panel System: Choose a solar panel system based on your energy needs and budget.
4. Calculate Energy Savings: Estimate the energy production of your solar system and calculate the potential savings based on reduced energy bills.
5. Consider Upfront Costs: Factor in the upfront costs of purchasing and installing the solar panels, including any incentives or tax credits.
6. Calculate Payback Period: Determine how long it will take for your energy savings to cover the upfront costs (payback period).
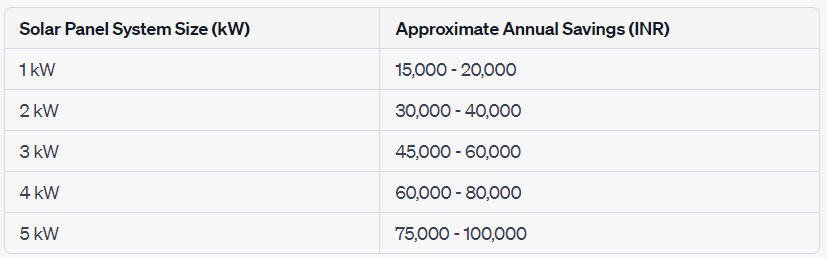
Please note that these savings are approximate and can vary based on factors like the system’s efficiency, electricity rates, and actual energy production. It’s advisable to consult with a solar installer to get a more precise estimate based on your specific location and energy needs.
Savings Over 25 Years
Solar panels have a long lifespan, typically ranging from 25 to 30 years. This longevity ensures that you can enjoy significant savings over the years. Here’s a breakdown of how savings accumulate over 25 years:
1. Energy Cost Savings: You will continue to save on your electricity bills for 25 years as your solar panels generate electricity.
2. Payback Period: The upfront costs of the solar installation are usually recovered within the first few years, after which your energy savings translate into direct financial benefits.
3. Tax Credits and Incentives: Any incentives or tax credits you receive are immediate savings that contribute to the overall financial benefits of solar.
Conclusion
Solar power is not only an environmentally friendly energy source but also a financially sound investment. Installing solar panels in Karnataka offers significant savings potential due to the state’s abundant sunlight, high electricity rates, and supportive policies and incentives.
Over 25 years, the cumulative savings from reduced energy costs, payback of upfront expenses, and incentives can be substantial. Whether you’re a homeowner or a business owner, harnessing solar power in Karnataka is a wise decision that can positively impact both your finances and the environment.